A&T Respiratory offers comprehensive courses, webinars, conference and resources for mastering respiratory care.
A&T Respiratory offers comprehensive courses, webinars, conference and resources for mastering respiratory care.
Copyright © 2026 A&T Respiratory Lectures All Rights Reserved
A&T Respiratory offers comprehensive courses, webinars, conference and resources for mastering respiratory care.
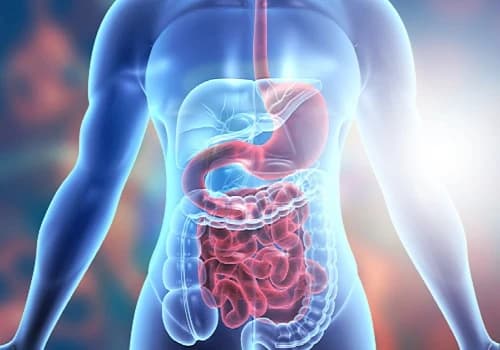
The digestive system is one of the most wide-ranging and complex systems of the body. It spans from the oral cavity to the rectum.
The primary function of the digestive system is to absorb nutrients like vitamins and minerals from the food we eat and get rid of the unwanted waste.
The health and optimum functioning of the gut is vital to our overall health. It is also linked to our mental health, immune system, and the risk of autoimmune diseases, skin conditions, endocrine dysfunctions, and cancer.
Healthcare experts emphasize taking care of the digestive health in order to protect the body against diseases. A majority of the illnesses occur due to the dysfunctions in the digestive system. Hence, there is a need to be aware of the signs, which indicate your digestive system is not functioning efficiently.
Here are the 5 common signs that point to an unhealthy digestive system.
Frequent stomach upsets with the occurrence of symptoms like bloating, gas, constipation, loose motions, and heartburn could be the sign of an inefficient digestive system.
All these symptoms indicate the inability of the stomach and intestine to digest the food and eliminate the waste from the body in an efficient manner.
Sleep disturbances like poor sleep quality or duration and insomnia might lead to chronic daytime fatigue. A larger share of a hormone called serotonin, which affects our mood and the sleep-wake cycle, is produced in the digestive tract.
Any damage to the gut could impair the healthy secretion of this hormone and thus, affect your ability to sleep well at night or stay alert and awake during the daytime.
If your immune system seems to respond in an abnormal way after eating certain foods, it could be a sign of an unhealthy gut. It indicates that your gut could be intolerant to those foods causing the immune system to trigger an abnormal response.
Some common examples of food intolerances and sensitivities include lactose intolerance caused due to the abnormal reaction of the immune system to lactose in milk and gluten intolerance caused due to the intake of gluten-containing foods.
Celiac disease is also a type of food intolerance that contributes to the development of chronic digestive problems due to the intake of gluten.
Chronic skin conditions such as psoriasis and eczema could be linked to an unhealthy digestive system.
Food allergies and a poor diet can cause chronic inflammation in the gut leading to the leakage of some proteins into the bloodstream. These proteins could irritate the skin leading to skin allergies and other chronic diseases like psoriasis and eczema.
An abrupt or unusual weight gain, as well as weight loss, could be a symptom of the disruptive digestive system.
An inefficiently functioning digestive system could impair the body’s ability to break down foods, absorb nutrients, store fats, and regulate blood sugar levels.
Insulin resistance and the tendency to overeat due to the reduced nutrient absorption can result in weight gain. Weight loss, on the other hand, could be a result of a condition called SIBO that is characterized by the overgrowth of harmful bacteria in the small intestine.
Our online respiratory webinars includes topics related to gut health and its impact on the risk of respiratory conditions such as asthma and COPD.
Our AARC Approved Live Respiratory CEUs are aimed at educating healthcare professionals about the common health concerns and how they are linked to the digestive system.
Chewing the food thoroughly and eating your meals slowly would help to promote the complete digestion of food and the absorption of nutrients. This would help to reduce digestive discomfort, enhance the supply of nutrients to the vital organs, and maintain a healthy and efficient gut.
Chronic mental stress could affect the health and functioning of all the organs of the body, including your stomach and intestine.
Some effective ways to lower mental stress include meditation, regular exercise like walking or swimming, aromatherapy, laughing, yoga, getting a massage, spending time with family or friends, and reducing your caffeine intake.
Not getting sufficient sleep could have a serious impact on the gut health, which, in turn, would contribute to the worsening of the sleep issues thus creating a vicious cycle.
It is important to follow a healthy sleep-wake routine and ensure you get at least 7 to 8 hours of sound and uninterrupted sleep every night to restore healthy gut functions.
Drinking plenty of water could have a beneficial effect on the mucosa of the stomach and intestines, and improve the balance of healthy bacteria in the gut.
Staying hydrated along with the use of prebiotics or probiotics could be a simple way to promote the gut health.
Eating High-fiber foods like legumes, peas, oats, beans, bananas, asparagus, berries, and leeks has been shown to create a positive impact on the gut health.
If you have symptoms like cramps, bloating, diarrhea, rashes, abdominal pain, nausea, acid reflux, and fatigue, you could be suffering from a food sensitivity or intolerance.
Identifying and eliminating the trigger foods would help to restore the healthy functions of the gut.
Eating a nutritious and balanced diet, avoiding food triggers, and maintaining the body's hydration are some effective ways to improve gut health. You can attend our Respiratory Therapy Continuing Education CEUs to learn more about the early signs of digestive issues and the most effective ways to manage them.